

The percentage of an element produced in the top producing country. Low = substitution is possible with little or no economic and/or performance impact Medium = substitution is possible but there may be an economic and/or performance impact High = substitution not possible or very difficult. The availability of suitable substitutes for a given commodity. A higher recycling rate may reduce risk to supply. The percentage of a commodity which is recycled. The number of atoms of the element per 1 million atoms of the Earth’s crust. This is calculated by combining the scores for crustal abundance, reserve distribution, production concentration, substitutability, recycling rate and political stability scores. The Chemical Abstracts Service registry number is a unique identifier of a particular chemical, designed to prevent confusion arising from different languages and naming systems.ĭata for this section been provided by the British Geological Survey.Īn integrated supply risk index from 1 (very low risk) to 10 (very high risk). Where more than one isotope exists, the value given is the abundance weighted average.Ītoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. This is approximately the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. The mass of an atom relative to that of carbon-12. The transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas phase without passing through a liquid phase.ĭensity is the mass of a substance that would fill 1 cm 3 at room temperature. The temperature at which the liquid–gas phase change occurs. The temperature at which the solid–liquid phase change occurs. The arrangements of electrons above the last (closed shell) noble gas.

These blocks are named for the characteristic spectra they produce: sharp (s), principal (p), diffuse (d), and fundamental (f). The atomic number of each element increases by one, reading from left to right.Įlements are organised into blocks by the orbital type in which the outer electrons are found. Members of a group typically have similar properties and electron configurations in their outer shell.Ī horizontal row in the periodic table. You can effortlessly find every single detail about the elements from this single Interactive Periodic table.A vertical column in the periodic table. Let me tell you how this Interactive Periodic Table will help you in your studies.ġ).
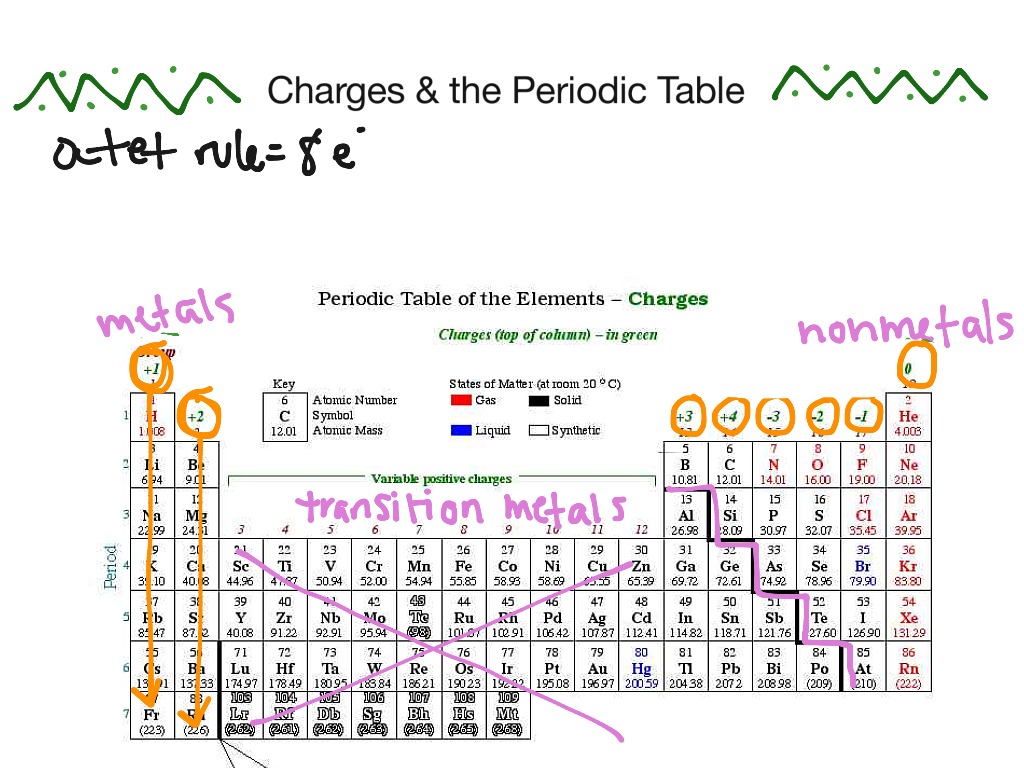
ELEMENT TABLE WITH CHARGES FREE
Number Elements Valence electrons 1 Hydrogen (H)Ģ 21 Scandium (Sc) 3 22 Titanium (Ti) 4 23 Vanadium (V) 5 24 Chromium (Cr) 6 25 Manganese (Mn) 7 26 Iron (Fe) 8 27 Cobalt (Co) 9 28 Nickel (Ni) 10 29 Copper (Cu) 11 30 Zinc (Zn) 12 31 Gallium (Ga) 3 32 Germanium (Ge) 4 33 Arsenic (As) 5 34 Selenium (Se) 6 35 Bromine (Br) 7 36 Krypton (Kr) 8 37 Rubidium (Rb) 1 38 Strontium (Sr) 2 39 Yttrium (Y) 3 40 Zirconium (Zr) 4 41 Niobium (Nb) 5 42 Molybdenum (Mo) 6 43 Technetium (Tc) 7 44 Ruthenium (Ru) 8 45 Rhodium (Rh) 9 46 Palladium (Pd) 10 47 Silver (Ag) 11 48 Cadmium (Cd) 12 49 Indium (In) 3 50 Tin (Sn) 4 51 Antimony (Sb) 5 52 Tellurium (Te) 6 53 Iodine (I) 7 54 Xenon (Xe) 8 55 Cesium (Cs) 1 56 Barium (Ba) 2 57 Lanthanum (La) 3 58 Cerium (Ce) 4 59 Praseodymium (Pr) 5 60 Neodymium (Nd) 6 61 Promethium (Pm) 7 62 Samarium (Sm) 8 63 Europium (Eu) 9 64 Gadolinium (Gd) 10 65 Terbium (Tb) 11 66 Dysprosium (Dy) 12 67 Holmium (Ho) 13 68 Erbium (Er) 14 69 Thulium (Tm) 15 70 Ytterbium (Yb) 16 71 Lutetium (Lu) 3 72 Hafnium (Hf) 4 73 Tantalum (Ta) 5 74 Tungsten (W) 6 75 Rhenium (Re) 7 76 Osmium (Os) 8 77 Iridium (Ir) 9 78 Platinum (Pt) 10 79 Gold (Au) 11 80 Mercury (Hg) 12 81 Thallium (Tl) 3 82 Lead (Pb) 4 83 Bismuth (Bi) 5 84 Polonium (Po) 6 85 Astatine (At) 7 86 Radon (Rn) 8 87 Francium (Fr) 1 88 Radium (Ra) 2 89 Actinium (Ac) 3 90 Thorium (Th) 4 91 Protactinium (Pa) 5 92 Uranium (U) 6 93 Neptunium (Np) 7 94 Plutonium (Pu) 8 95 Americium (Am) 9 96 Curium (Cm) 10 97 Berkelium (Bk) 11 98 Californium (Cf) 12 99 Einsteinium (Es) 13 100 Fermium (Fm) 14 101 Mendelevium (Md) 15 102 Nobelium (No) 16 103 Lawrencium (Lr) 3 104 Rutherfordium (Rf) 4 105 Dubnium (Db) 5 106 Seaborgium (Sg) 6 107 Bohrium (Bh) 7 108 Hassium (Hs) 8 109 Meitnerium (Mt) 9 110 Darmstadtium (Ds) 10 111 Roentgenium (Rg) 11 112 Copernicium (Cn) 12 113 Nihonium (Nh) 3 114 Flerovium (Fl) 4 115 Moscovium (Mc) 5 116 Livermorium (Lv) 6 117 Tennessine (Ts) 7 118 Oganesson (Og) 8 Free Gift for you: Interactive Periodic Table Valence Electrons Chart for All Elements Atomic (Where you will get the HD images along with the explanation).
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/PeriodicTableCharge-BBG-58b5c80a3df78cdcd8bbb6c8.png)
If you want a Periodic table with Valence electrons, then visit Periodic table with Valence electrons labeled in it. But for most of the transition and inner transition elements, the valence electrons are the electrons present in the shells outside the noble gas core.For main group elements (i.e s-block and p-block elements), the valence electrons are the electrons present in the outermost orbit.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
